Endodontics
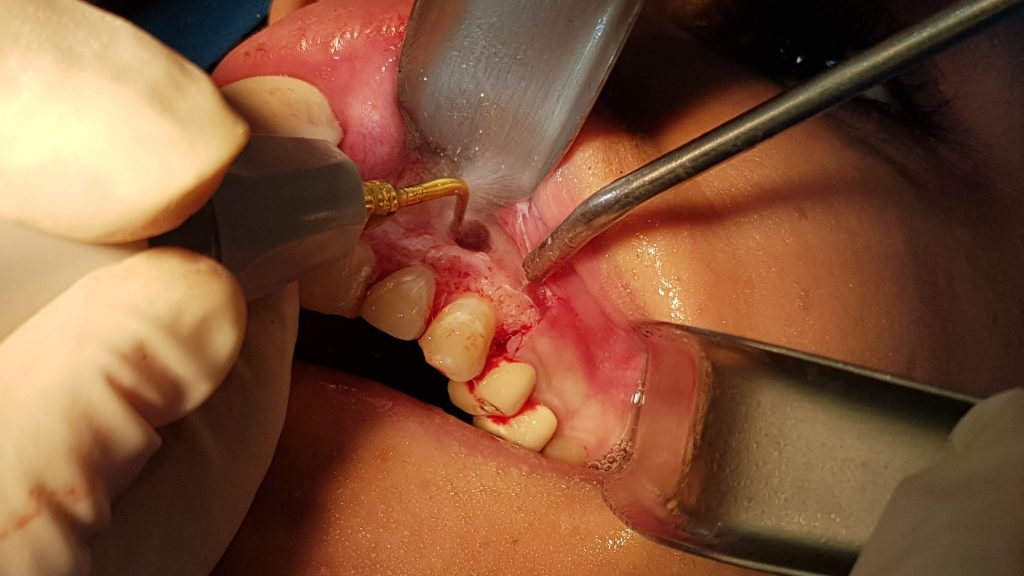
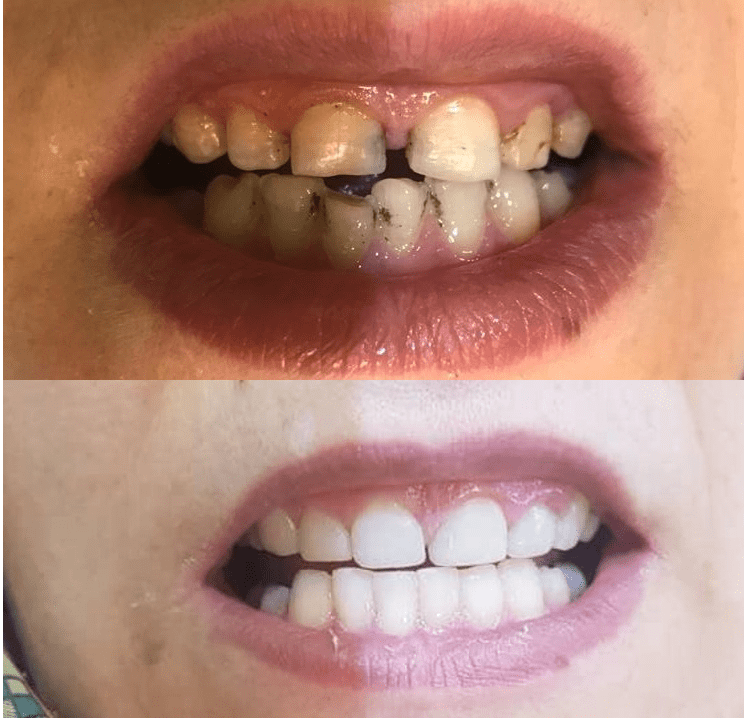
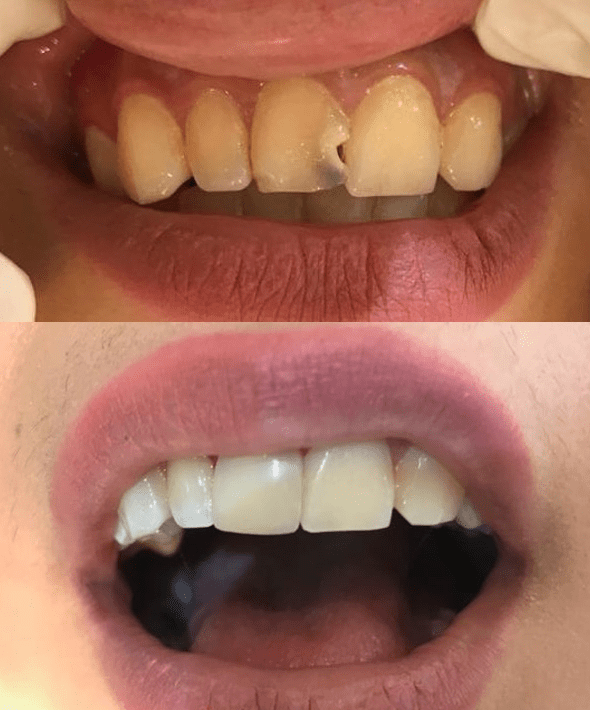
Root canal treatment (also known as endodontic therapy, endodontic treatment, or root canal therapy) is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which results in the elimination of infection and the protection of the decontaminated tooth from future microbial invasion. Root canals, and their associated pulp chamber, are the physical hollows within a tooth that are naturally inhabited by nerve tissue, blood vessels and other cellular entities. Together, these items constitute the dental pulp Endodontic therapy involves the removal of these structures, the subsequent shaping, cleaning, and decontamination of the hollows with small files and irrigating solutions, and the obturation (filling) of the decontaminated canals. Filling of the cleaned and decontaminated canals is done with an inert filling such as gutta-percha and typically a eugenol-based cement. Epoxy resin is employed to bind gutta-percha in some root canal procedures. Endodontics includes both primary and secondary endodontic treatments as well as periradicular surgery which is generally used for teeth that still have potential for salvage.
RCT
APEXOGENESIS
RE RCT
APEXIFICATION